一、什么是内部类?
内部类是在一个类中的类,类的声明可在类中或方法中。
内部类的特点
优点:
- 内部类可以方便的访问外部类的隐式成员变量
- 一个类作为内部类是一种很好的信息隐藏,例如静态内部类需要使用 类名.内部类 引出,成员内部类使用 对象.内部类 引出
- 内部类可以实现单继承的局限性
缺点:
- 结构复杂
结构复杂体现下内部类的访问、内部类中使用外部类的成员变量等方面。
二、四种内部类
成员内部类
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void broadcastRepeat(String msg) {
Beee b = new Beee(msg);
//开始哔哔
b.start();
}
// 复读机,重复Person想要说的信息
// 普通内部类通过外部类的对象创建, 引用属于对象,每个内部类对象都是不一样的
// 成员变量是static是必须使用final修饰
public class Beee extends Thread {
private String msg;
public Beee(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(name);
while (true){
// 为什么能使用外部类的name,因为在调用构造器时把Person对象传入了进来,通过字节码可以看出来,下面对应着Beee的构造器
//INVOKESPECIAL elltor/basic/innerclass/normal/Person$Beee.<init> (Lelltor/basic/innerclass/normal/Person;Ljava/lang/String;)V
System.out.println(msg + " --" + name);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
// test
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person lisi = new Person("lisi", 18);
//lisi.broadcastRepeat("大家好哇~");
// 通过对象创建普通内部类,然后使用(看上去有些奇怪,因为这是对象持有的类,所以通过对象可以创建,而静态类使用类名.创建)
// 注意每个对象的内部类都是不一样的
Person.Beee bb = lisi.new Beee("bb create by lisi");
bb.start();
}
}
静态内部类
public class Person4 {
String name;
int age;
public Person4(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void broadcastRepeat(String msg) {
Beee b = new Beee(msg);
//开始哔哔
b.start();
}
// 静态内部类不能使用非静态的变量
// 静态内部内能够被其他类使用,而普通内部类只能在定义它类中使用
public static class Beee extends Thread {// 复读机,重复Person想要说的信息
private String msg;
public Beee(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
//test
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1
Person4 p = new Person4("lisi",19);
p.broadcastRepeat("hello everyone~ ");
// 2
Person4.Beee bee = new Person4.Beee("在Person4外使用");
bee.start();
}
}
局部内部类
public class Person2 {
String name;
int age;
public Person2(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void broadcastRepeat(String msg) {
// 不能使用publi或private修饰,可以使用final修饰
// 该类对于完结来说完全隐藏,每调用此方法创建一次且使用一次
class Beee extends Thread {// 复读机,重复Person想要说的信息
private String msg;
public Beee(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Beee b = new Beee(msg);
//开始哔哔
b.start();
}
}
// test
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person2 p = new Person2("lisi",18);
p.broadcastRepeat("大家好哇~");
}
}
匿名内部类
public class Person3 {
String name;
int age;
public Person3(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 匿名内部类1,匿名生成一个子类覆盖父类的方法
public void broadcastRepeat(String msg) {
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
// 匿名内部类2,匿名创建接口对象
public void broadcastRepeat2(String msg) {
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
new Thread(run).start();
}
}
// test
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person3 p = new Person3("lisi",18);
//p.broadcastRepeat("hello~");
p.broadcastRepeat2("hello2~");
}
}
内部类的使用
在 JDK 的集合框架中大量使用到内部类
并不只有内部类,接口也可以定义在一个接口里。
Map 中定义的 Entry 接口
public interface Map<K,V>{
interface Entry<K,V> {
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
}
}
HashMap 中的内部类
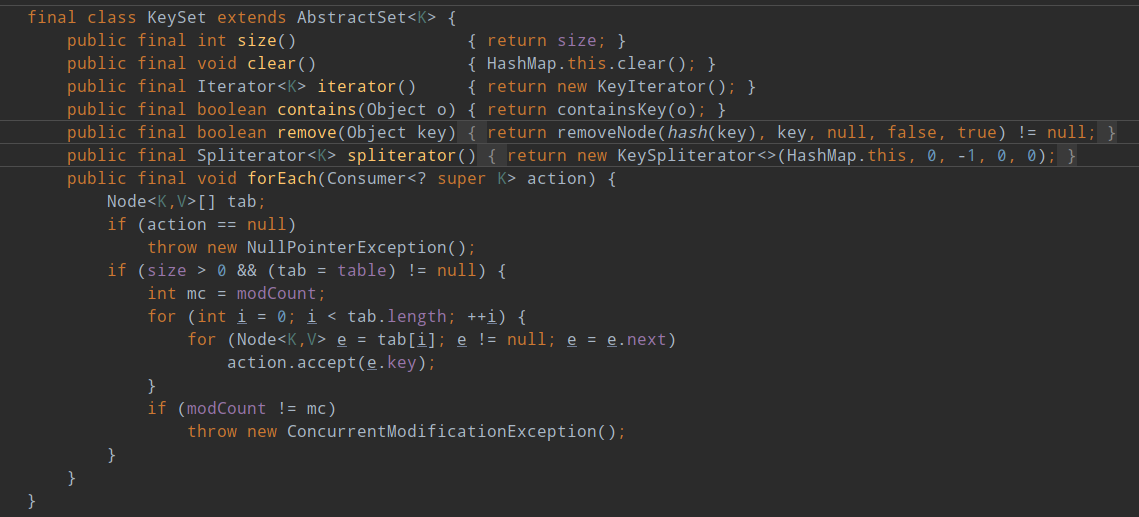
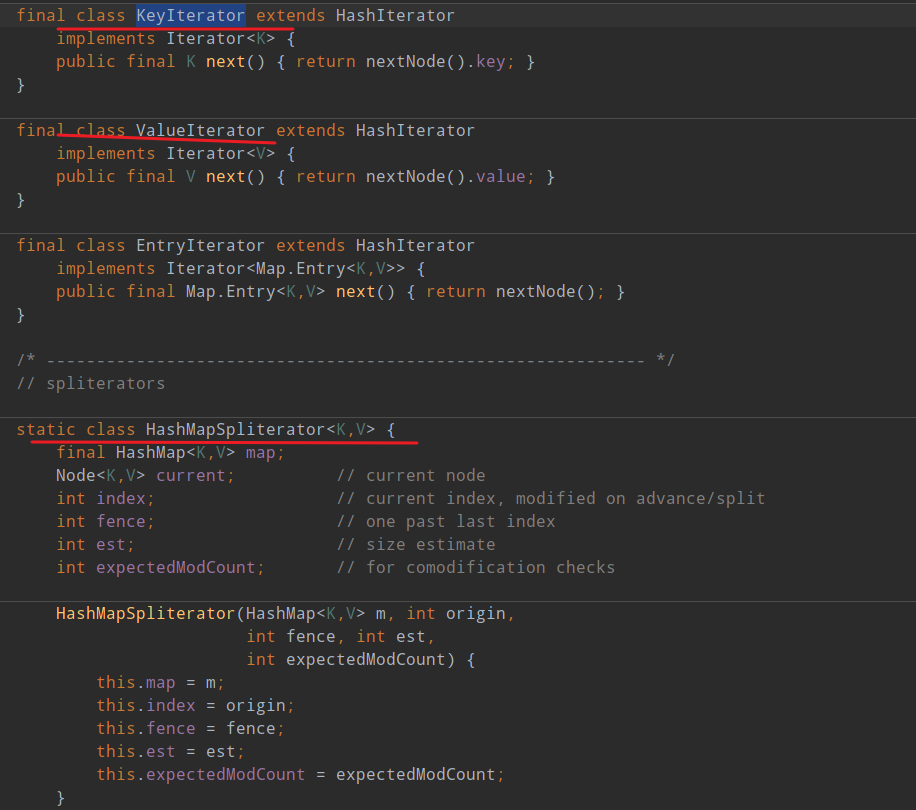
构建者模式(Builder)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/58093669
public class Computer {
private final String cpu;//必须
private final String ram;//必须
private final int usbCount;//可选
private final String keyboard;//可选
private final String display;//可选
private Computer(Builder builder){
this.cpu=builder.cpu;
this.ram=builder.ram;
this.usbCount=builder.usbCount;
this.keyboard=builder.keyboard;
this.display=builder.display;
}
public static class Builder{
private String cpu;//必须
private String ram;//必须
private int usbCount;//可选
private String keyboard;//可选
private String display;//可选
public Builder(String cup,String ram){
this.cpu=cup;
this.ram=ram;
}
public Builder setUsbCount(int usbCount) {
this.usbCount = usbCount;
return this;
}
public Builder setKeyboard(String keyboard) {
this.keyboard = keyboard;
return this;
}
public Builder setDisplay(String display) {
this.display = display;
return this;
}
public Computer build(){
return new Computer(this);
}
}
//省略getter方法
}